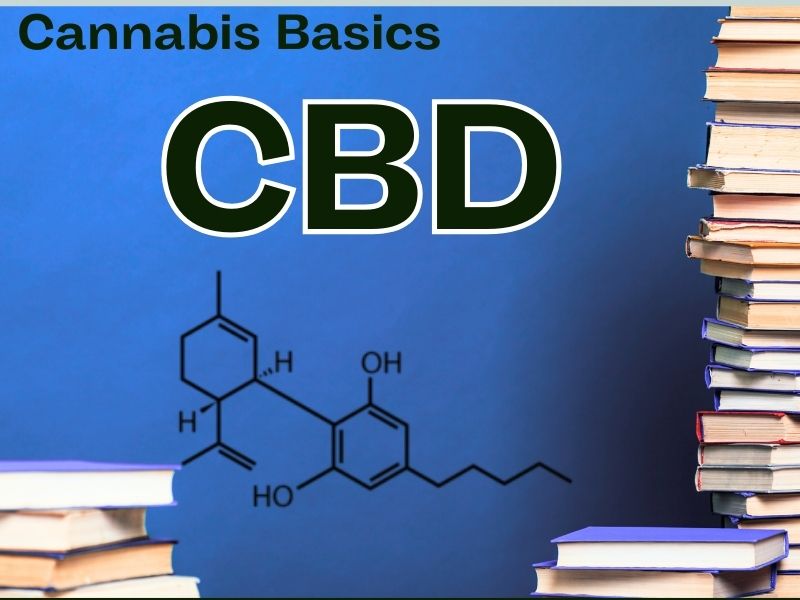
Cannabidiol (CBD) has captured global attention as a versatile natural compound with profound therapeutic potential. Its journey—from obscurity to prominence—is rich with scientific intrigue, accidental discoveries, impactful personal stories, and evolving legal landscapes.
Historical Context
The cannabis plant, from which CBD is derived, has been utilized medicinally for thousands of years, documented in ancient China, Egypt, and India for conditions ranging from pain relief and inflammation to anxiety and insomnia. However, modern scientific understanding began in the early 20th century. In 1940, American chemist Roger Adams first identified CBD, though he wasn’t fully aware of its precise chemical structure or therapeutic potential. The full isolation and structural elucidation of CBD occurred in 1963 when Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, an Israeli scientist often dubbed “the father of cannabis research,” clearly defined its chemical properties and therapeutic promise. Mechoulam’s groundbreaking work paved the way for decades of research into cannabinoids, laying the foundation for modern cannabinoid science.
Breeding CBD Out and Back In
Throughout the late 20th century, recreational breeding significantly altered cannabis plants, focusing primarily on increasing THC—the psychoactive compound—and inadvertently reducing CBD content. CBD nearly vanished from most cannabis strains, overlooked and misunderstood by growers and consumers alike, who often associated potency strictly with psychoactive effects.
In the early 2000s, CBD-rich strains began resurfacing thanks to dedicated cultivators, patient advocacy groups, and researchers aiming to explore cannabis’s medicinal properties without the psychoactive effects of THC. Their concerted efforts sparked renewed interest and significant research into CBD’s diverse medical benefits. This resurgence led to the proliferation of specialized hemp cultivars specifically bred for their high CBD and minimal THC content, making therapeutic cannabis more accessible and acceptable worldwide.

Rediscovery and Charlotte Figi’s Story
CBD burst into global consciousness through the poignant story of Charlotte Figi, a young girl suffering from Dravet Syndrome, a severe form of epilepsy characterized by frequent, debilitating seizures unresponsive to traditional treatments. Her seizures dramatically decreased upon using a CBD-rich cannabis extract, later named “Charlotte’s Web,” after her. Charlotte’s remarkable improvement became a catalyst, raising global awareness and encouraging clinical investigation into CBD’s medicinal potential, reshaping perceptions worldwide and fueling broader legislative reforms around medical cannabis.
Charlotte’s story significantly influenced public opinion, contributing to the destigmatization of cannabis-derived treatments and inspiring numerous families struggling with similar conditions to pursue CBD as a viable therapeutic alternative.
FDA Approval and Epidiolex
Charlotte’s success, supported by growing scientific research and advocacy, ultimately led to significant medical breakthroughs, culminating in the U.S. FDA’s approval of Epidiolex in 2018. Epidiolex became the first cannabis-derived medication approved by the FDA, specifically for treating rare, severe forms of epilepsy, including Dravet and Lennox-Gastaut syndromes. This landmark decision legitimized CBD within mainstream medicine, prompting rigorous clinical standards and paving the way for potential future cannabinoid-based therapies.
Major Health Benefits and Supporting Research
Inflammation
CBD is well-documented for its anti-inflammatory properties, largely attributed to its ability to interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system and various inflammatory pathways. Numerous preclinical studies and animal models have demonstrated CBD’s effectiveness in reducing chronic inflammation by modulating immune responses, cytokine production, and oxidative stress pathways. Research increasingly suggests CBD’s potential therapeutic use in treating inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and multiple sclerosis, significantly improving patients’ quality of life.

Addiction and Cravings
CBD has emerged as a promising treatment for addiction management due to its impact on brain circuits involved in reward, craving, and relapse. Clinical trials have found CBD effective in reducing cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and anxiety associated with abstinence for substances such as opioids, tobacco, cocaine, and alcohol, offering a novel and promising approach to addiction recovery strategies. This aspect of CBD’s therapeutic potential offers considerable hope in addressing the ongoing opioid epidemic and other substance abuse crises globally.
Anxiety Disorders
CBD’s anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) properties have been widely studied, with robust evidence indicating its efficacy in treating generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). A significant Brazilian study found that CBD notably reduced anxiety levels in participants undergoing stressful public speaking tasks. Additional research highlights CBD’s potential to modulate serotonin receptor signaling, suggesting it may function similarly to conventional anxiolytic medications but with fewer side effects, making it a promising alternative or complementary therapy.
Epilepsy
Perhaps the most researched therapeutic area, CBD has proven exceptionally effective in reducing seizures in drug-resistant epilepsy cases. Extensive Epidiolex clinical trials conclusively demonstrated significant reductions in seizure frequency and severity, offering a transformative alternative for patients who previously had limited options. The efficacy and safety profiles established through these studies have reinforced CBD’s medical legitimacy, encouraging further investigations into its potential broader applicability in neurological disorders.
Neuropathy
Research consistently indicates CBD’s potential to alleviate neuropathic pain, which remains notoriously difficult to manage with conventional treatments. Clinical and preclinical studies on diabetic neuropathy, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, and HIV-associated neuropathy have shown promising outcomes. CBD’s ability to modulate pain perception and reduce inflammation and neuroinflammation positions it as a promising therapeutic option, potentially filling significant gaps in current pain management protocols.
Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD)
Emerging research highlights CBD’s therapeutic potential for individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASD), showing encouraging results in early clinical trials. Preliminary clinical evidence suggests improved behavioral symptoms, reduced aggression, enhanced communication abilities, and decreased anxiety levels among ASD patients using CBD treatments. Although the evidence remains preliminary, these promising outcomes are prompting larger-scale clinical trials aimed at further validating CBD as an adjunctive therapy in autism management.
Conclusion
From historical obscurity to a celebrated natural therapeutic, CBD’s journey highlights the intricate relationship between science, culture, medicine, and policy. With ongoing and robust research continuing to unveil new applications and insights, CBD stands as one of modern medicine’s most promising natural allies, promising continued discoveries and significantly improved quality of life for individuals around the globe.